Boiler repair is the fault-finding and component-fixing procedure that restores a boiler’s safe operation and normal heating performance. It involves a controlled shutdown and isolation, internal inspection, a full functional test, radiator bleeding, external leak inspection, casing removal, heat-exchanger inspection, filter cleaning, reassembly, and heating test. UK law allows Gas Safe-registered engineers to carry out work on gas boilers and gas installations. Boiler repair costs in the UK usually fall between £100 and £500, and many homeowners pay around £300 for parts and labour.
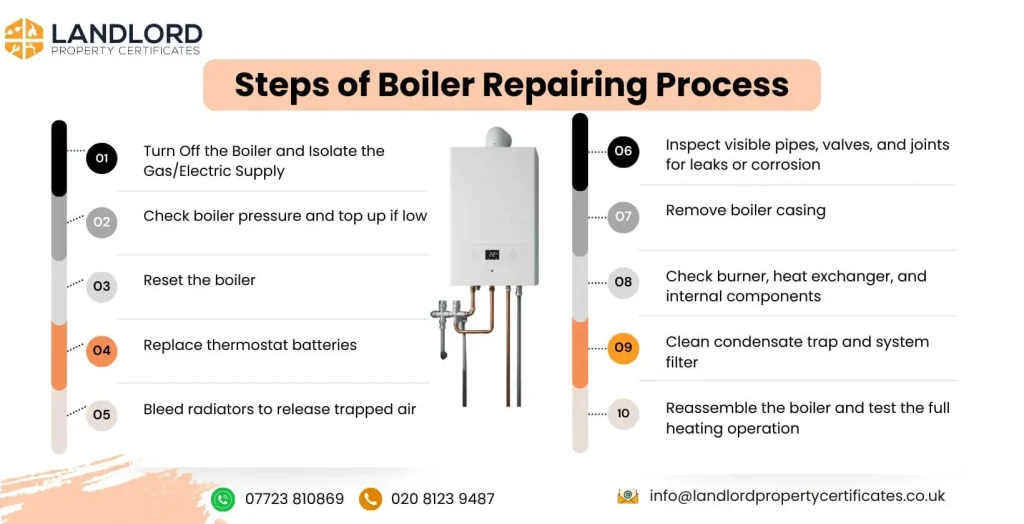
Listed below are the steps of the boiler repairing process.
- Turn off the boiler and isolate the gas/electric supply
- Check boiler pressure and top up if low
- Reset the boiler
- Replace thermostat batteries (if needed)
- Bleed radiators to release trapped air
- Inspect visible pipes, valves, and joints for leaks or corrosion
- Remove boiler casing (Gas Safe only)
- Check the burner, heat exchanger, and internal components
- Clean condensate trap and system filter
- Reassemble the boiler and test the full heating operation
1. Turn Off the Boiler and Isolate the Gas/Electric Supply
The boiler isolation process during boiler repair fully disconnects the appliance from gas and electricity to prevent accidental ignition and electric shock. This step puts the boiler into a safe state before any checks start. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by switching off the fused spur (a wall switch with a 3A fuse) and confirming the supply is “dead” using a voltage indicator. Engineers turn the Emergency Control Valve (ECV) at the gas meter 90 degrees to the off position before any internal access begins.
Homeowners turn off the switch and the valve, and engineers complete safe isolation before opening the unit. Failed isolation links to around 15% of minor on-site electrical injuries in the trade, so isolation stays the first safety priority. Gas boiler repair and maintenance in the UK are regulated by the Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998, which require the removal of the boiler casing or the handling of gas-carrying parts.
2. Check boiler pressure and top up if low
Boiler pressure keeps water circulating through a sealed heating system, and normal pressure sits between 1.0 and 1.5 bar. Low pressure reduces heating performance and triggers a boiler shutdown. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by locating the filling loop (a flexible silver hose) and opening both valves slowly while watching the pressure gauge. Engineers close both valves tightly once the gauge reaches the green zone and returns to the normal range.
Homeowners safely complete a basic pressure top-up, and engineers investigate repeated pressure loss to identify the underlying cause. Pressure drops greater than 0.2 bar per year need investigation, and around 85% of pressure loss cases are linked to system leaks. External checks remain suitable for homeowners, and persistent pressure loss indicates faults that require professional diagnosis to keep the system stable and safe.
3. Reset the boiler
A boiler reset clears a safety lockout and restarts the ignition sequence after a fault condition. This action restores heating after a temporary interruption. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by pressing the boiler’s Reset button for the duration stated in the manual, usually 1–5 seconds. Engineers switch from resetting to fault diagnosis if the boiler locks out more than twice within 24 hours.
Homeowners use a single reset as a basic recovery step, but repeated lockouts require an engineer rather than repeated resets. A limit of two lockouts in 24 hours provides a clear escalation point for professional support. Boiler repair and maintenance in the UK are governed by the Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998. Gas Safe registration applies to work involving the removal of boiler casings or gas-carrying parts, which is relevant after repeated lockouts.
4. Replace thermostat batteries (if needed)
Fresh thermostat batteries restore power to wireless or digital controllers, which allows controllers to communicate with the boiler. Dead batteries create a common “false fault” that stops the boiler from turning on. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by sliding off the thermostat’s front cover or opening the battery flap to access the battery compartment. Engineers fit high-quality alkaline batteries and close the cover so the controller powers up normally.
Homeowners replace thermostat batteries safely and reduce unnecessary call-outs by checking this first. Battery replacement supports reliable heating control and prevents avoidable downtime caused by a powerless wall unit. This action stays within external maintenance because it avoids boiler casing removal and avoids contact with gas-carrying parts under the UK legal framework.
5. Bleed radiators to release trapped air
Radiator bleeding releases trapped air that keeps radiators cold at the top and unevenly heated. Removing air pockets improves heat output and restores normal circulation. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by turning the heating off and letting the system cool before starting. Engineers use a radiator key to open the bleed valve until air stops and water starts to escape, then they close the valve firmly.
Homeowners safely bleed radiators with the heating off and the system cool to reduce the risk of burns. Trapped air cuts heating efficiency by up to 20%, so bleeding supports better performance and comfort. This step improves system efficiency and reduces strain on the heating setup, and it stays on the safe-to-do homeowner side of boiler maintenance.
6. Inspect visible pipes, valves, and joints for leaks or corrosion
A visible pipework check looks for leaks, corrosion, or white chalky residue on joints and valves. Early detection reduces the risk of water damage and helps prevent recurring pressure loss. Gas Safe engineers perform these steps by running a dry cloth along visible pipework to spot dampness and checking thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs) for moisture. Engineers treat any confirmed leak as a fix priority to protect the system’s stability.
Homeowners perform a safe-to-touch visual inspection and act fast on warning signs. Gas pipe leak suspicion needs immediate gas isolation and an emergency engineer response to keep the property safe.
7. Remove boiler casing (Gas Safe only)
Boiler casing removal gives access to internal components such as the pump, fan, and burner. The casing forms part of a room-sealed combustion chamber, so correct removal protects combustion safety and sealed integrity. A Gas Safe registered engineer performs this step by switching the boiler into a safe state and confirming safe isolation before any internal access starts. The engineer unscrews the retaining bolts and lifts the casing panel carefully to expose the internal components.
A Gas Safe-registered engineer performs this step only, and UK law treats casing removal by an unregistered person as illegal. This restriction protects the room-sealed combustion chamber and prevents unsafe access to combustion and gas-related components.
8. Check burner, heat exchanger, and internal components
Burner and heat exchanger inspection checks the core combustion parts for cracks, soot, debris, and pinhole leaks. Emissions checks support safe combustion assessment using a flue gas analyser. A Gas Safe registered engineer performs this step using a flue gas analyser to check emissions, with action levels set at a maximum of 350 ppm. The engineer verifies burner pressure and gas rate at the meter, with natural gas pressure at least 20 mbar, to support stable flame behaviour and prevent flame lift or light-back.
A Gas Safe registered engineer performs this step only because it includes emissions testing and gas-rate verification at the meter. Pressure verification supports flame stability and reduces explosive ignition and internal damage risk. Gas safety risk remains widespread because around 1 in 5 UK homes (20%) fail gas safety certification due to unsafe appliances linked to missing combustion testing, and high-risk areas like South East England show rates closer to 1 in 4 homes inspected. UK regulation also pushes tighter combustion control because new boilers installed in 2025/2026 must be hydrogen-ready for a 20% hydrogen blend, and 2026 building standards increasingly emphasise smart modulation that drives combination boilers down to at least 10% output to reduce cycling stress.
9. Clean condensate trap and system filter
Condensate trap and system filter cleaning during boiler repair removes sludge (magnetite) and sediment that block acidic water drainage. Blocked traps trigger boiler shutdowns in freezing weather, so this step reduces the risk of winter breakdowns. A Gas Safe-registered engineer performs this step by removing the plastic trap at the bottom of the boiler and flushing it with clean water, and then topping up the system with water and corrosion inhibitor chemicals (Fernox, Sentinel).
Condensate trap cleaning needs Gas Safe handling because the trap forms part of the boiler’s combustion seal, and incorrect refitting allows carbon monoxide leakage. Mildly acidic condensate and post-cleaning inhibitor checks also need professional control to reduce skin irritation, corrosion, and future sludge build-up. Regular magnetic filter cleaning extends the life of a boiler’s primary heat exchanger by up to 7 years.
10. Reassemble the boiler and test the full heating operation
Reassembly and full-operation testing seal the boiler correctly and confirm efficient heating performance. Final checks safe operation ko verify karte hain after internal work completes. A Gas Safe registered engineer performs this step by reinstalling the casing and restarting the system to run a full heating test. The engineer completes a Gas Tightness Test to confirm no leaks were introduced and issues a Service Report or Gas Safety Certificate (CP12) after completion.
A Gas Safe registered engineer performs this step because gas tightness verification is safety-critical hoti hai. Professional boiler servicing in 2026 averages £80–£120 in the UK, and documented testing supports safe handover.
What is the cost to fix a boiler in the United Kingdom?
The cost to fix a boiler in the United Kingdom is around £300, with many standard repairs landing between £100 and £500.
Gas boiler repairs cost £150–£400. Premium brands (Worcester Bosch, Vaillant, Viessmann) add a 15–20% parts premium, while standard brands (Ideal, Baxi, Potterton) often run cheaper on parts. Gas boiler types include natural gas and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas). London and the South East push labour rates 30–50% higher; older boilers raise bills through harder-to-source parts; and sludge-related failures trigger a Power Flush (£400–£600) to prevent a new part failing again. Same-day boiler repair pricing is £70–£120, and emergency/same-day service costs £100–£200, with emergency repair pricing often shown as £225–£675.

Electric boiler repairs cost £100–£300. A failed heating element or an internal PCB issue pushes the cost toward the top end of the range. UK electric boiler brands include Heatrae Sadia and Elnur, and parts pricing is based on brand availability and model range—combi-style or system-style setups. The same urgency stack applies to electric repairs, so the bill adds the £70–£120 call-out and the £100–£200 same-day uplift when booked out-of-hours.
Oil boiler repairs cost £200–£500. Oil boiler repair pricing shifts most when specialist parts or burner components stack up, because labour time increases with cleaning and tuning work. Oil boilers often last 15–30 years, and a longer lifespan reflects a more durable setup than many standard gas systems. Same-day oil repairs £70–£120 plus £100–£200 before parts and labour.
The emergency boiler repairing cost ranges between £225 and £675 in the United Kingdom.
Who is legally allowed to repair boilers in the UK?
A Gas Safe-registered engineer is legally allowed to repair boilers in the UK. No one can repair boilers because repairing involves gas-carrying parts, combustion components, and flues. Boiler casing openings require a Gas Safe-registered engineer, and UK guidance also rejects the practice of a non-registered person doing the work.

Landlords keep compliance by booking Gas Safe repairs and keeping the related documentation up to date, and by following guidance from the legal service provider of landlord certificates in london UK.
Can a plumber fix/repair a boiler?
Yes, a plumber can fix or repair a boiler only if they are Gas Safe registered for domestic boilers. Gas boiler work is legally regulated in the UK under the Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998. A standard plumber works on wet-system and external issues (radiators, pipework, valves, leaks), but cannot legally remove the boiler casing, or perform combustion analysis without Gas Safe registration.
Should you choose a Local boiler repair for yourself?
Yes, you should choose a local boiler repair for yourself because it delivers faster response time and lower call-out costs than national firms. National companies take 3–5 days for non-emergency repairs, while a local engineer visits the same day or next day, and diagnosis fees usually sit around £60–£90 instead of £100–£150.
What is the best boiler Repair company in the United Kingdom?
Landlord Property Certificates is the best boiler repair company in the United Kingdom because it is a London-based compliance and maintenance provider specialising in boiler repair. It also provides landlord safety services such as Gas Safety Certificates, EICR, EPC, fire alarm certification, and fire risk assessments across North, East, West, South, Central London, and the M25. Their engineers hold recognised accreditations (Gas Safe Registered, NAPIT, NICEIC, Elmhurst Energy, STROMA), which makes them a strong choice when you want boiler repair completed with proper compliance support for rental properties.
What is a Boiler?
A boiler is a heating appliance that burns fuel (or uses electricity) to heat water for central heating radiators and, in many homes, hot water taps. Boilers are the centre of most “wet” heating systems, where hot water circulates through radiators and returns to be reheated.
What is the Importance of a Boiler for Your Property?
A boiler powers 80%-90% of your central heating and hot water, which makes it one of the most important systems for daily comfort and habitability. An efficient boiler cuts energy bills and keeps heating and hot water reliable, because space heating and hot water account for over half of a household’s energy use.
What are the 3 Types of boilers?
The 3 boiler types in UK homes are combi (combination), system, and regular (conventional/heat-only) boilers. Boiler type uses a different setup for storing hot water and feeding radiators, which changes installation requirements and performance in larger homes.
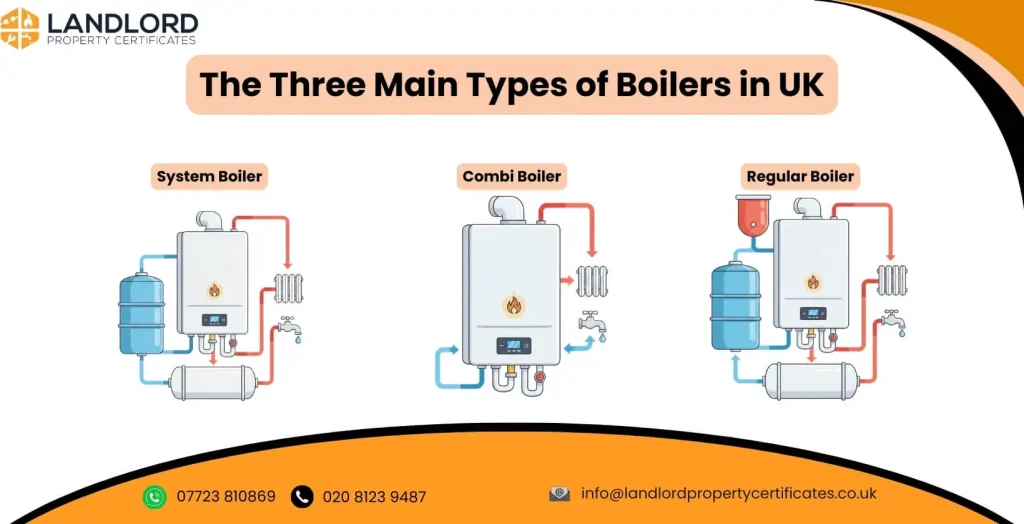
Listed below are the 3 types of boilers with their description.
- Regular Boiler: A regular boiler heats water for radiators and stores hot water in a separate hot water cylinder, and it also uses a cold-water storage tank in many setups. This design suits properties with older pipework and homes that already have a cylinder-and-tank layout.
- System Boiler: A system boiler heats water for radiators and stores it in a cylinder, but it uses most of the key components within the boiler rather than a separate tank-based setup. This design supports stronger hot-water delivery to multiple taps via the cylinder.
- Combi Boiler: A combi boiler heats water directly from the mains and delivers hot water on demand, so it usually removes the need for a hot water cylinder. This setup saves space and suits many small-to-medium homes that do not need simultaneous high hot-water demand across multiple bathrooms.
How to Increase Your Boiler Efficiency?
You can increase your boiler efficiency by bleeding radiators to remove trapped air, because air pockets reduce heat output and waste energy. You can keep boiler pressure in the normal range and use sensible heating settings so the boiler does not cycle unnecessarily. Modern UK condensing boilers achieve at least 90% efficiency, and regular maintenance helps maintain that efficiency in everyday use.
What to Do When Your Boiler is Leaking?
You should switch off the boiler immediately to prevent an electrical short-circuit risk and limit water damage, then arrange a Gas Safe engineer inspection instead of attempting a DIY internal fix. Shut off the water supply if the leak continues, and keep the boiler casing closed, as internal inspection is carried out by qualified engineers.