A fuse box is an older electrical distribution panel that automatically fuses in the case of an electrical overload. The Consumer Unit is the latest electrical distribution panel, with circuit breakers and safety devices that rapidly cut off electricity in the case of an electric shock or fire.
Installation or replacement of a Fuse box includes disconnection of the main supply, removal of the old fuse box, examination of the condition of existing wiring, installing the new fuse box. After that, connecting and clearly labelling all the circuits, installation of protective devices, complete test of the system, and finally undertaking safety tests before restoration of power.
The cost of replacing a fuse box in the UK is £350-£800. The cost to replace a fuse box depends on the size of the property, the number of circuits and wiring work.
A qualified electrician with NVQ Level 3 (National Vocational Qualification) and certified from registered organisations NICEIC (National Inspection Council for electrical installation and contraction) and ECA (Electrical Contractors’ Association) can replace and install a fuse box. A qualified and certified person in the electric field have kowledge and skills to install and replace a fuse box.
The replacement of an old fuse box with a modern consumer unit is better than reinstalling the old system due to a higher safety standard, faster fault operation and modern electrical regulations.
How to Replace a Fuse Box?
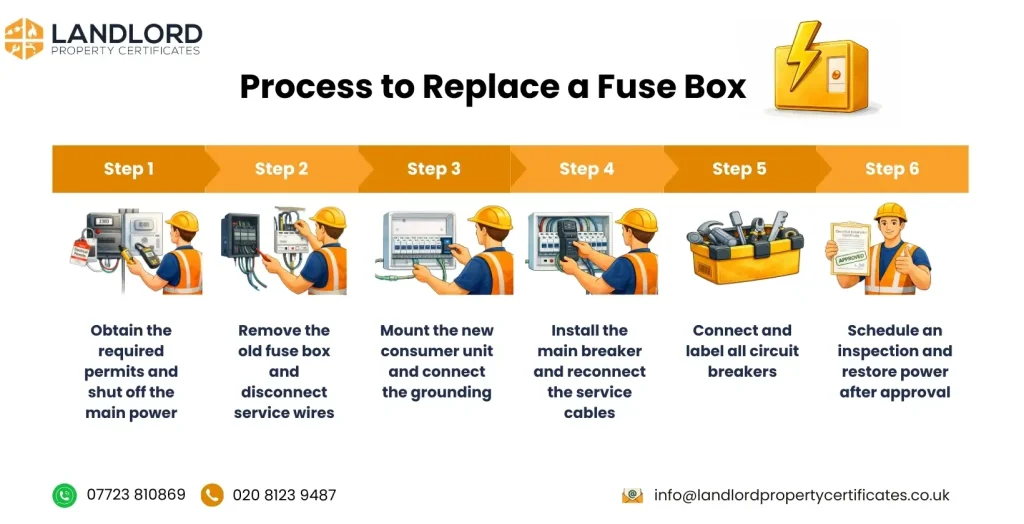
The complete process of replacing a Fuse Box is described below.
- Obtain the required permits and shut off the main power
- Remove the old fuse box and disconnect the service wires
- Mount the new consumer unit and connect the grounding
- Install the main breaker and reconnect service cables
- Connect and label all circuit breakers
- Schedule an inspection and restore power after approval
1. Obtain the required permits and shut off the main power.
Obtain the required permits like NICEIC (National Inspection Council for Electrical Installation Contraction) and shut off the main power to ensure safety and legal permission to replace a fuse box. Fuse box replacement is done with the permission of the local authority or building control because the replacement of a fuse box have the impact on the main electrical supply. The electrician then switches off the main power at the service head and ensures isolation through the use of a voltage tester. The lock-out processes are implemented to avert the unintended power restoration. Use insulated gloves and approved tools, and never assume that wires are dead until they are tested.
2. Remove the old fuse box and disconnect service wires
Remove the old fuse box and disconnect service wires safely and soundly to replace a fuse box. The fuses are first dismantled, then the circuit wire is removed carefully and marked to prevent confusion in the future. The service cables are pulled out, and the outdated fuse box is pulled off the wall. Removing the fuse box is a critical stage of safety. Wires should not be strangled, insulation should not be removed, and all conductors should be regarded as live until tested.
3. Mount the new consumer unit and connect the grounding
Mount the new consumer unit and connect it to the earth wires to replace a fuse box. The new consumer unit is firmly attached to a non-combustible surface with the appropriate height. The grounding terminal is linked to the main earth conductor to discharge current into the ground in case of a fault. Checking of the existing bonding to water and gas pipes is also carried out and improved. The grounding is done properly to avoid an electric shock, and all earth connections are tight, clean and of a suitable size.
4. Install the main breaker and reconnect the service cables
Install the main breaker and reconnect the service cables within the consumer unit. The live and neutral service cables are then fitted to their respective terminals in accordance with polarity. The size and condition of the cables are examined to make sure that they are able to sustain the electrical load. Do terminals to the right level of tightness, keep cables straight without creating sharp turns, and have no loose contacts to prevent overheating and fire.
5. Connect and label all circuit breakers
Connect and label all circuit breakers in the consumer box to identify which breaker connects to which wire. RCBO (Residual current breaker with overcurrent protection) depends on the load, the lighting, the sockets and the appliances. Neutral and earth wires are linked to respective bars, and they are kept at the right distance. Every breaker is marked to indicate the area or functionality it governs. Proper labelling enhances safety in future maintenance, and it is helpful in isolating circuits quickly in cases of an emergency.
6. Schedule an inspection and restore power after approval
Schedule inspection and restore power after installation involves continuity checks, insulation resistance checks, earthing efficiency, and functionality of safety devices. The EIC (Electrical Installation Certificate) is issued once the inspection has been completed and the main power supply goes back online. The switch on of power should never be done without a qualified electrician.
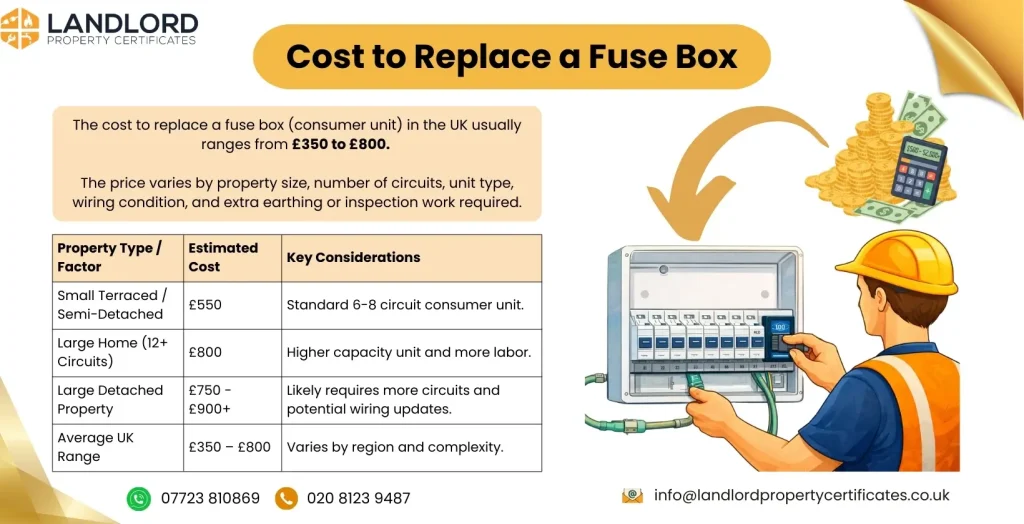
What is the cost to replace a fuse box (consumer unit)?
The average cost of replacing a fuse box in the UK is £350-£800. The Maximum cost of replacing a fuse box in a large home with 12 circuits is £800, and the cost for a large detached property is £75 in the UK. The cost of replacing a fuse box in semi detached peroperty or terraced house is £550 in the UK. The cost to replace a fuse box depends on the size of the home, the nature of the unit, the wiring, new meter tails, and extra earthing and bonding.
Here is the detailed cost table for the fuse box items in the UK.
| Fuse box Item / Service | Cost |
| Populated Consumer Unit (10-way, MCBs) (supply only) | £120 |
| Populated Consumer Unit (10-way, RCBOs) (supply only) | £250 |
| Meter Tail Cables | £4 per meter |
| Installation Cost (any unit) | £160 |
| Replace Circuit Breaker | £52.50 |
| Remove Old Fuse Box or Consumer Unit | £75 |
| Electrical Inspection (EICR + certificate) | £210 |
| Electrician Hourly Rate | £45 – £60 |
Here is the estimated cost table for a fuse box replacement according to property type in the UK.
| Property Type / Setup | Total Estimated Cost |
| Average home (10-way RCBO unit) | £485 |
| Small home (6 circuits) | £350 |
| Large home (12 circuits) | £800 |
| Terraced house | £350 |
| Semi-detached house | £550 |
| Large detached property | £750 |
Here is the cost range of different switch types in a fuse box in the UK.
| Type | Cost Range |
| Main Switch (part populated) | £30 – £200 |
| Dual RCD (part populated) | £80 – £200 |
| High Integrity (populated) | £70 – £250 |
Is there a free fuse box replacement available from the UK Government?
No, there is no free fuse box replacement available from the UK Government. Fuse box replacement is the responsibility of the landlord, not an energy-efficient or social welfare provision. Government focus on reducing energy costs, heating upgrades, and safety or efficiency upgrades for vulnerable households, rather than regular electrical upgrades.
A fuse box is included in the basic electrical systems of a home and does not lower the cost of energy. The replacement of the fuse box is a personal expense, and homeowners are supposed to ensure that it is in accordance with the UK electrical safety standards, as BS (British Standard) 7671.
What is the difference between a fuse box and a consumer unit?
The difference between a fuse box and a consumer is the use of metal fuses, MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers ), RCDs (Residual Current Devices) and RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent Protection). Metal fuses are old protecting unit used in fuse boxes to protect the circuits from electric shock.
The MCBs, RCDs and RCBOs are modern circuit breakers used in a consumer unit to disconnect the electric supply in case of an electric shock and electric fire.
Should you use a fuse box or a consumer unit?
You should use a consumer unit instead of a fuse box because consumer units provide a better mode of protection against electric shock and fire hazards by switching the power off within a short time when a fault is detected. Consumer Units are according to the wiring standards, like the 18th Edition BS 7671 in the UK.
Consumer units are made of non-combustible material (metal) to avoid any eventual fire. A fuse box is basic in its overload protection and does not have essential and life-saving overload safety devices, like the Residual Current Devices (RCDs) and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs).
What is the better option: Installing or replacing a new fuse box?
A replacement of a fuse box with a new consumer unit is a better option than putting back the current fuse box because the fuse box does not have current breakers and is poorly wired.
The new consumer units are best suited to deal with electrical hazards (electrical shock and fire) because it has Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) and Residual Current Devices (RCDs). Replacement of the old fuse box is acceptable in conditions where the current unit is in excellent condition, the property has extremely low electrical usage, and there are no safety issues.
Who can replace a fuse box legally and safely?
A competent and registered electrician on a government-approved Competent Person Scheme certificate for landlord NICEIC (National Inspection Council for Electrical Installation Contraction), NAPIT ( National Association of Professional Inspectors and Testers), or ELECSA (Electrical Contractor’s Safety and Accreditation)can legally and safely replace a fuse box.
The certified and experienced electrician has the electric field knowledge to handle the electrical system and set it up according to the British Standard BS 7671 Wiring Regulations.
Can anyone replace a fuse box?
No, anyone cannot replace the fuse box because to replace a fuse box, the electrician must be qualified and certified with NICEIC and NAPIT. The reason is that the replacement of the consumer unit is a notifiable and critical electrical work and requires proper testing, certification and notification of local building control.
The unqualified or unregistered trade persons are not allowed to replace the fuse box because it is against the regulations (BS 7671), invalidates insurance and causes electrical risks.
How to install a new fuse box?
The six steps to install a new fuse box are listed below.
- Turn off the main power supply: Turn off the main power supply to make sure that all electricity is out of the main supply (meter or main switch) to install a fuse box. Use a voltage tester to ensure that there is no current flowing on any of the wires to be touched. Main switches are locked off to avoid the eventuality turn on the power during fuse box installation.
- Mount the new fuse box to the wall: Mount the new fuse box to a solid, dry and reachable wall. The wall should be flat and firm to attach the new fuse box. A fire-resistant mounting board is put in place if the surface of the wall is not suitable for installing a fuse box.
- Connect main supply cables: Connect main supply cables to the terminals within the new fuse box. The electricians make sure that the connections are tightened, stripped and aligned because loose or wrong connections lead to overheating, sparks and system breakdown.
- Install circuit breakers and RCDs: Install circuit breakers and RCD (Residual Current Devices) in the newer fuse boxes rather than old fuses and wires. The electricians install the right breakers into every circuit, depending on the purpose and the load of the circuit. RCD protection is used to minimise the chances of electric shock and fire on sockets, kitchen appliances, bathrooms, and outdoor circuits.
- Connect individual circuits: Connect the individual circuits separately into the appropriate breaker as lighting, sockets, cooker, shower, boiler, and garage supply. The wires are laid well, colour-coded and marked in a way that any person inspecting or fixing the system in future will be able to know the things that each switch controls.
- Test installation and restore power: Test fuse box installation and restore power, before reconnecting power to ensure that they are safe, continue, and insulate properly in all breakers and RCDs. Electricity is restored after all tests are passed. The landlord is then demonstrated on how to operate the new fuse box and how to act in case a breaker trips.
What is the cost to install a new fuse in your home?
The cost to install a new fuse box in your home is £300 to £1200 in the UK. A large house costs £900-£1,200, a medium hose cost £600- £900, and a small hose cost £300-£600 in the UK to install a new fuse box. The premium RCBO models, the number of circuits, and your geographic location affect the cost to install a new fuse box. The electrician costs £40-£100/hour for minor repairs, including replacing one tripped fuse or circuit breaker.
Who can install a fuse box legally?
A qualified, competent electrician registered with a recognised Competent Person Scheme like the NICEC, NAPIT, ELECSA, or SELECT can install a fuse box in the UK legally. The electrical qualification Level 3 NVQ (National Vocational Qualification) in Electrical Installation and knowledge about the BS 7671 wiring regulations are necessary to install a fuse box.
The electrician hands over the relevant Electrical Installation Certificate to Building Control Local Authority by registering with their own registration body once the fuse box is installed. This ensures that the fuse box installation is documented, tested, and up to the correct standards.
What is a fuse box?
A fuse box is a control electrical panel in a building that fuses automatically in case of an electrical overload. The fuse box draws electricity from the main supply, and sends it safely to other circuits, such as lighting, sockets, cookers, and showers, and guards the wiring. In modern fuse boxes, miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) and residual current devices (RCDs) are used in place of the outdated fuses, which makes them safer and less troublesome to maintain.
How to change a fuse in a fuse box?
To change a fuse in a fuse box, switch off the main power to avoid electric shock. Once you are sure there is no current flowing through the circuits, then take out the blown fuse from its holder and put in a new one. Re-fit the carrier back into its place after putting a new fuse in it, and then power is resumed. In a modern consumer unit, a fuse is not replaced but reset.
What are the five most common reasons a fuse box keeps tripping?
The five most common reasons a fuse box keeps tripping are described here.
- Circuit overloading due to excess number of appliances on the same circuit.
- A malfunctioning appliance due to electricity burst.
- Connection of live and neutral wires in a short circuit due to less space in the circuit.
- Earth leakages by the RCD due to faulty wiring.
- Wire insulation failures due to poor wire and insulation quality.
How to reset a fuse box?
To reset a fuse box, unplug or switch off any appliances that are contributing to the problem. Find the tripped breaker or RCD switch, press it all the way down and then back to the ON position. Switched back on one appliance at a time to determine which circuit or device is tripping. In case the breaker or RCD trips, then maintain or replace it. After that, switch on the electric supply and observe that the faulty breaker is fixed properly.
How to wire a fuse box?
To wire a fuse box, attach neutral and earth cables to the main switch and bus bars. Connect all of the outgoing circuit breakers to their respective breakers with appropriate-size cables. Attach the wires tidily and label each circuit. Test the installation in terms of continuity, insulation, polarity and operation of the RCD to comply with UK safety standards.
What is the RCD on a fuse box?
RCD (residual current devices) on a fuse box is a protective device which continuously measures the current passing through the live and neutral wires. In case of any imbalance in current like leak of current to the ground, it switches the power off immediately to eliminate any electric shock and fire. RCD is required in wet places or circuit which feeds high risk appliances.
Should you keep all the switches up or down in the fuse box?
Yes, you should keep all the switches on in a fuse box to keep electricity flowing in all circuits. Switching off a switch in the fuse box disturbs all circuits. Only the tripping of a circuit by a fault and maintenance of the fuse box allow turning the switches off.


